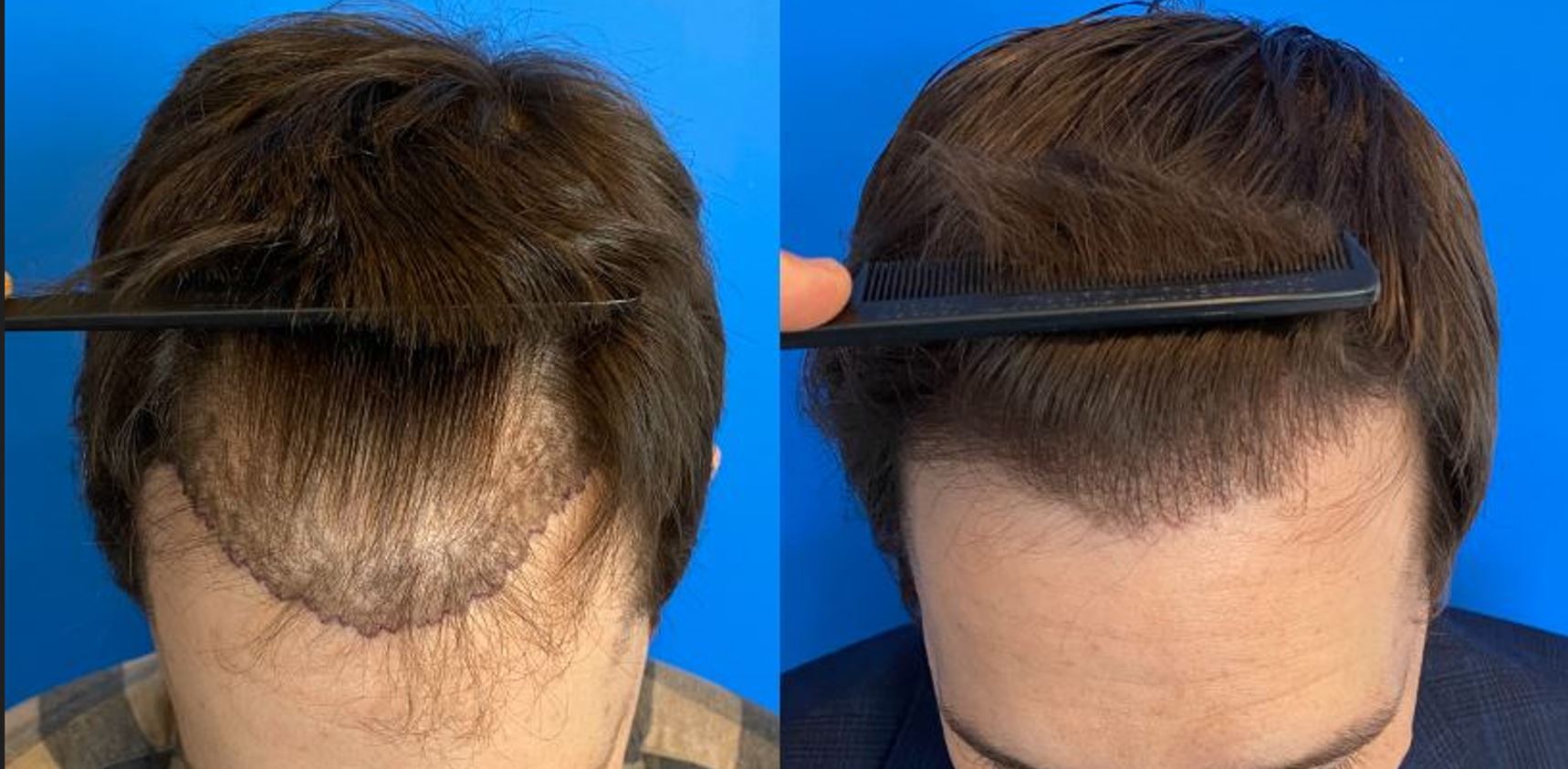
Hair loss is a common concern that can impact one’s confidence and self-esteem. However, the field of hair restoration offers a range of solutions to combat this issue and revitalize your look. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various hair restoration options, including surgical and non-invasive treatments, providing insights to help you make informed decisions for a confident and revitalized appearance.
Understanding Hair Loss
Before delving into hair restoration solutions, it’s essential to understand the common causes of hair loss:
1. Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia):
Hereditary factors play a significant role in male and female pattern baldness, leading to gradual hair thinning and loss.
2. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, often associated with pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and certain medical conditions, can contribute to hair loss.
3. Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and alopecia areata, can result in hair loss.
4. Medications:
The side effects of some medications, including those used for cancer, arthritis, depression, and heart problems, may lead to hair loss.
5. Poor Nutrition:
Inadequate nutrition and vitamin deficiencies can impact the health of hair follicles, contributing to hair loss.
Surgical Hair Restoration Options
For those seeking more permanent and transformative solutions, surgical hair restoration options are available:
1. Hair Transplant Surgery:
Hair transplant surgery involves the extraction of hair follicles from the donor area (usually the back of the scalp) and their transplantation to the recipient area with thinning or no hair. This procedure provides a natural-looking and long-lasting solution.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
FUE is a modern hair transplant technique that involves the extraction of individual hair follicles for transplantation. It is known for its precision and minimally invasive nature, leaving tiny, dot-like scars.
3. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and transplanting them to the recipient area.
Non-Invasive Hair Restoration Treatments
Non-invasive treatments offer effective solutions for individuals who prefer less invasive approaches to combat hair loss:
1. Topical Medications:
FDA-approved topical medications, such as minoxidil, can promote hair growth and slow down hair loss. These medications are applied directly to the scalp.
2. Oral Medications:
Prescription medications like finasteride can be taken orally to inhibit the action of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a major contributor to hair loss.
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
LLLT devices, such as laser caps or helmets, use low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. This non-invasive method is often used as part of a comprehensive hair restoration plan.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the PRP into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
5. Hair Growth Shampoos and Topicals:
Specialized shampoos and topicals containing active ingredients like ketoconazole, saw palmetto, and biotin can contribute to maintaining a healthy scalp environment and promoting hair growth.
Choosing the Right Hair Restoration Option
When considering hair restoration, it’s essential to assess your individual needs, preferences, and the extent of your hair loss. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Degree of Hair Loss:
The extent of your hair loss will influence the most suitable restoration option. Surgical methods may be more appropriate for advanced hair loss, while non-invasive treatments are effective for early to moderate stages.
2. Budget:
Consider your budget, as surgical hair restoration procedures tend to be more expensive than non-invasive treatments.
3. Expectations:
Have realistic expectations about the outcomes of different treatments. Surgical procedures provide more transformative results, while non-invasive options may require ongoing maintenance.
4. Comfort with Invasiveness:
Assess your comfort level with invasive procedures. Non-invasive treatments are generally less disruptive, with quicker recovery times.
5. Consultation with Professionals:
Consult with experienced hair restoration professionals to assess your specific needs and receive personalized recommendations.
Conclusion
Hair restoration is a dynamic field with a variety of options to address the diverse needs of individuals experiencing hair loss. Whether opting for surgical methods like hair transplants or non-invasive treatments such as topical medications and laser therapy, there are effective solutions to revitalize your look. By understanding the causes of hair loss, exploring available treatments, and considering personal preferences, individuals can make informed decisions on their journey to a confident and revitalized appearance.
